2669. Rotation
An array of size n × m is
given. Rotate it 90° clockwise.
Input. The first line contains two positive integers n
and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 50).
Each of the next n lines
contains m nonnegative integers, each not exceeding 109 –
the elements of the array.
Output. Print the resulting array in the same format as in
the input.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
3 41 2 3 45 6 7 8
9 10 11 12 |
4 3 9 5 1 10 6 2 11 7 3 12 8 4 |
SOLUTION
two-dinensional array
Algorithm analysis
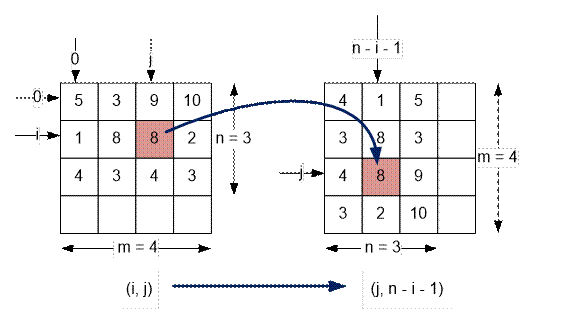
When matrix a is
rotated 90 degrees clockwise, the element at position (i, j) moves to the position (j, n
– i – 1) in matrix b.
If the original matrix a
has dimensions n × m, then the resulting matrix b will have
dimensions m × n. The indexing of elements in both matrices starts
from 0.
Algorithm implementation
Declare the input array a
and the resulting reversed array b.
#define MAX 55
int a[MAX][MAX], b[MAX][MAX];
Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(j = 0; j < m; j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
Reverse array a and store the result in b.
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(j = 0; j < m; j++)
b[j][n-i-1] = a[i][j];
Print the reversed array b.
printf("%d %d\n",m,n);
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j
< n; j++)
printf("%d
",b[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}